OUG = EMERGENCY ORDINANCE no. 195 of December 12, 2002 (Road Traffic Code)
Regulation = REGULATION for the implementation of OUG 195/2002 (Road Traffic Code Regulation)
2. shoulder - the lateral strip between the limit of the carriageway and the edge of the road platform;
14. public road - any land communication route, except for railways, specially arranged for pedestrian or road traffic, open to public circulation; the roads that are closed to public circulation are signalled at the entrance with visible inscriptions;
23. carriageway - the portion of the road platform intended for the circulation of vehicles; a road may include several carriageways completely separated from each other by a dividing area or by a level difference;
33. sidewalk - the longitudinal space located on the lateral part of the road, visibly separated from the carriageway by a level difference or without a level difference, intended for pedestrian circulation;
(5) At the entrance to a road that is not open to public circulation, its owner or administrator is obliged to install, in a visible place, a sign with the meaning "No entry" and a panel with the inscription "Road closed to public circulation".
If you cannot/do not want to watch the AUDIO-VIDEO version of the course, you can read the text version illustrated with images.
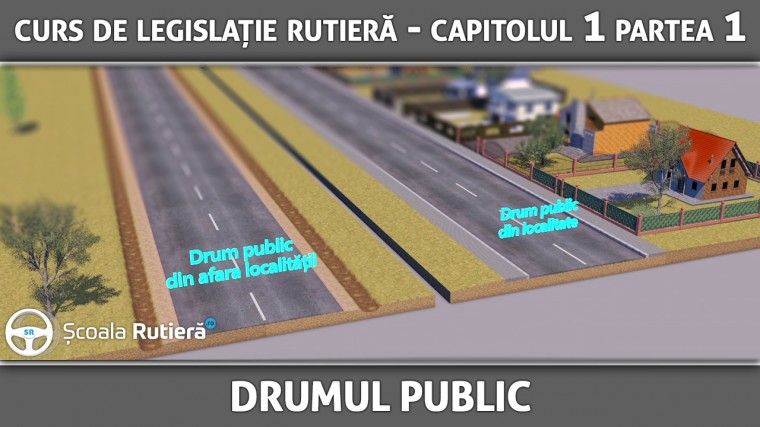
Public road (art. 6 point 14 of the OUG) - is any land communication route, except for railways, specially arranged for pedestrian or road traffic, open to public circulation.
TO REMEMBER:
- not all roads can be public roads, examples of roads that are not public: forest roads or agricultural roads;
The roads that are closed to public circulation are signalled at the entrance by the sign with the meaning "No entry" and an additional panel with the inscription "Road closed to public circulation" (art. 3 paragraph 5 of the Regulation).

- the road traffic code regulates circulation only on public roads.
The public road outside built-up areas has the following component parts:

The public road in built-up areas has the following component parts:

ROAD IN ALIGNMENT: is the portion of a road in a straight line, which has no curves.

ROAD IN CURVE: is the bend of the public road in the shape of a circular arc that connects two road segments in alignment.

ROAD WITH GRADIENTS: is the public road that climbs or descends.

In this example we have a portion of road without gradients, followed by an uphill, meaning the portion of road that climbs, after which we have a level road, which is the portion of road that neither climbs nor descends, after which we have a downhill, which is the portion of road that descends and at the end we have another portion of road without gradients.
To remember that on the uphill you climb and on the downhill you descend.
Leave a comment